“`html
Essential Guide to Keto Enol Tautomerism: Modern Insights for 2025
Understanding Keto-Enol Tautomerization
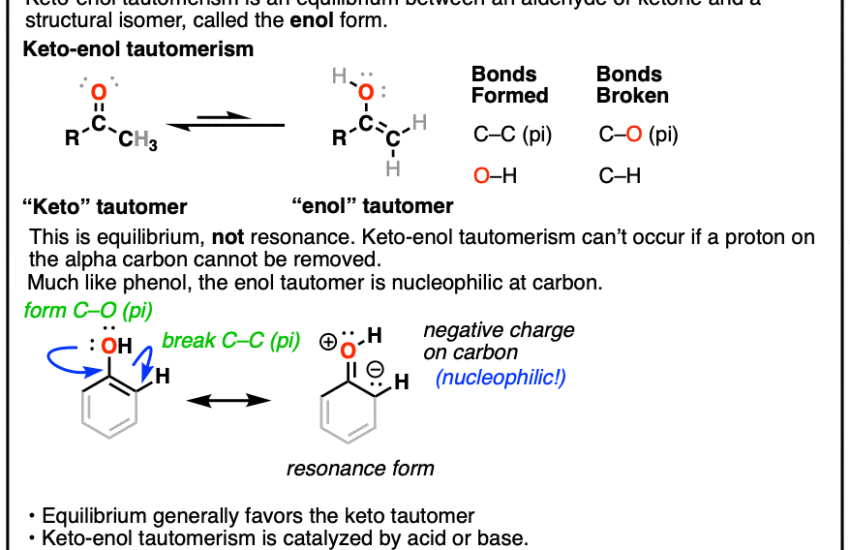
Keto-enol tautomerization is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, representing the reversible conversion between keto and enol forms of carbonyl compounds. This process involves the shifting of a proton and the rearrangement of the molecular structure, a shift that can dramatically affect the chemical reactivity and stability of compounds. The keto form typically exhibits a higher thermodynamic stability compared to its enol counterpart, often making the keto-enol ratio favor the keto form in equilibrium. However, under specific conditions, such as catalytic environments or when certain functional groups are present, the enol form may predominate. Recognizing the nuances of tautomeric equilibrium is essential for chemists working on reaction mechanisms and synthesis strategies.
Keto Form and Enol Form Stability
The stability of the keto and enol forms largely depends on the electronic environment around the carbonyl group. The keto form, bearing a double bond between carbon and oxygen, generally exhibits more pronounced resonance stabilization. In contrast, the enol form, characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group and a carbon-carbon double bond, can be stabilized by hydrogen bonding and intramolecular interactions. Factors such as the acidity and hybridization of substituents impact the equilibrium constant, ultimately dictating the reaction dynamics and selectivity in synthesis methods. In many cases, the enol form participates in chemical bonding and structural isomerism, thus presenting intriguing avenues for synthetic organic chemistry.
Tautomeric Conversion Dynamics
The transition between keto and enol forms is influenced by various reaction conditions, often highlighted in mechanistic studies. Tautomerization typically involves a two-step mechanism: proton transfer followed by the reorganization of electrons, often facilitated by acid-base catalysis. The kinetics of this transformation can showcase competing pathways, and understanding these can lead to insights into reaction rates and the factors affecting both kinetic and thermodynamic control. It is crucial for chemists attempting to manipulate these pathways for desired outcomes. For example, organic compounds with specific functional groups might favor enolization, which can lend unique properties to the reaction intermediates involved in chemical synthesis.
Tautomeric Equilibrium and Chemical Reactivity
One critical aspect of keto-enol tautomerism is the consideration of chemical equilibrium in various reactions and transformations. The equilibrium constant quantitatively describes the ratio of concentrations of products to reactants at equilibrium. In keto-enol reactions, this is vital not just to understand stability but also to showcase how certain reaction environments can shift the balance in favor of either the keto or enol form. For example, the presence of electrophiles may enhance enolate formation, driving the formation of useful intermediates in asymmetric synthesis.
The Role of Chemical Equilibrium in Tautomerism
In the context of tautomerism, chemical equilibrium is not a static state but a dynamic one that reflects the balance of forward and reverse reactions. Various factors influence this equilibrium, including solvent properties, temperature, and the presence of catalysts. Reaction pathways that favor thermodynamic stability will often lead to the predominance of the more stable keto form, while conditions favoring kinetic control might yield enol forms. Consequently, understanding the nuances of reaction thermodynamics and spatial arrangements, such as molecular geometry and sterics, plays a vital role in predicting and enhancing reaction outcomes.
Applications of Keto-Enol Tautomerism
The versatility of keto-enol tautomerism extends into a wide array of applications in organic synthesis and biochemical pathways. It is commonly leveraged in various synthetic strategies to create diverse products and intermediates, such as in the formation of enolates that can participate in nucleophilic addition reactions. Furthermore, the significance of tautomerism stretches into pharmaceutical chemistry, wherein the bioavailability of drug compounds may hinge on their tautomeric forms. Thus, understanding tautomerization kinetics is essential for optimizing reaction conditions and developing drug candidates.
Kinetics and Mechanistic Insights into Tautomerization Reactions
To fully appreciate the complexities of keto-enol tautomerism, one must explore the kinetics involved in these equilibrium processes. The rates at which these transformations occur can provide vital information on the underlying mechanistic pathways. Factors such as solvent polarity, temperature, and the presence of acids or bases influence the tautomerization kinetics and thus govern the reaction mechanism. By comprehensively exploring these dynamics, chemists can tailor their approach depending on desired products and stability considerations.
Proton Transfer and Reaction Mechanisms
Proton transfer is a pivotal step in the keto-enol tautomerization process, often marking the transition between the two forms. This reaction involves several key aspects, including solvent interactions and the role of catalysts, which can help stabilize the transition states. In cases of acid-base catalysis, the protonation of a carbonyl oxygen can facilitate the formation of the enol, enhancing reaction rates. Detailed mechanistic pathways elucidate how molecular configurations, substituent effects, and external environments play critical roles in determining whether the reaction favors the kinetic or thermodynamic product.
Transformation Reactions and Spectroscopic Analysis
The study of tautomerism also entails a myriad of transformation reactions that can be monitored through various spectroscopic analysis techniques. Tools like NMR spectroscopy and UV-Vis can be employed to visualize the dynamic distribution between keto and enol forms and to dissect the reaction pathways. Gaining insights into the energy profiles and reaction intermediates assists researchers in refining synthetic organic chemistry methodologies. Analytical strategies are crucial in understanding how structural isomerism impacts chemical properties and reactivity trends.
Key Takeaways on Keto-Enol Tautomerism
- Keto-enol tautomerization is an essential process for understanding molecular stability and reactivity in organic chemistry.
- The kinetics and reaction pathways are influenced by various factors, including solvent effects, electronic environment, and presence of catalysts.
- Applications of tautomerism in organic synthesis and pharmaceutical preparations highlight its practical significance in chemical transformations.
- Proton transfer mechanisms reveal intricacies in mobility and the significance of bond stability in tautomeric forms.
FAQ
1. What is keto-enol tautomerism?
Keto-enol tautomerism describes the dynamic equilibrium between keto (carbonyl) and enol (hydroxyl) forms of a compound. The process is characterized by proton transfer and is significant for understanding chemical reactivity and structural stability in various compounds.
2. How does acid-base catalysis influence keto-enol tautomerization?
Acid-base catalysis facilitates proton transfer, impacting the rate and equilibrium of keto-enol tautomerism. The presence of a strong acid or base can accelerate the conversion process, thereby favoring the formation of either the keto or enol form depending on the reaction conditions.
3. What role does equilibrium constant play in tautomeric relationships?
The equilibrium constant quantifies the relative concentrations of keto and enol forms at equilibrium. It provides insights into the stability and reactivity of these tautomeric forms, reflecting how changes in solvent or temperature can impact their distribution.
4. How is tautomerism applied in pharmaceutical chemistry?
Tautomerism has crucial implications in the design of drug compounds, as the bioactivity may depend on the predominant form (keto or enol). Understanding tautomeric stability helps in predicting drug behavior and optimizing formulations to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
5. What methods are used to study keto-enol tautomerism?
Various analytical and spectroscopic techniques like NMR, UV-Vis, and mass spectrometry are employed to investigate keto-enol tautomerism. These methods aid in understanding the molecular dynamics, reaction kinetics, and equilibria of different tautomeric forms in organic compounds.
“`